Perovskite Solar - Page 5
Researchers develop unique HTMs to enhance device stability of PSCs
Researchers from Thailand's Mahidol University, Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi and Synchrotron Light Research Institute have presented two novel air-stable hole transporting materials (HTMs) based on a spiro[fluorene-9,9′-xanthene] (SFX) core functionalized with N-methylcarbazole (XC2-M) and N-hexylcarbazole (XC2-H) rings.
These HTMs were synthesized via a straightforward, three-step process with good overall yields (∼40%) and low production costs. To further reduce device cost, carbon back electrodes were employed. The resulting PSCs, with a structure of FTO/SnO2/Cs0.05FA0.73MA0.22Pb(I0.77Br0.23)3/HTM/C, achieved power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of 13.5% (XC2-M) and 10.2% (XC2-H), comparable to the reference spiro-OMeTAD device (12.2%).
Scientists mark a successful launch of perovskite PV into space
Together with his collaborators at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and Technical University of Berlin, Dr. Felix Lang from the University of Potsdam previously launched perovskite tandem solar cells into space to test their performance with extreme radiation levels and temperature cycles. Recently, he successfully received the first data from his experiment.
July 9, 2024 was the day of the maiden launch of the new Ariane 6 rocket from Guiana Space Centre by ESA. On-board a satellite was a special solar cell experiment. The satellite itself was successfully released one hour and six minutes after launch. “The solar cells have survived launch and started to produce energy, even without perfect alignment to the sun,” says Felix Lang, who celebrates this first success with his junior research group at the chair of Prof. Dr. Dieter Neher, funded by a Freigeist-Fellowship of the Volkswagen Foundation.
Fellow Energy plans to build a perovskite solar cell and module factory in China
Jiangsu Xiehang Energy Technology (Fellow Energy/Xiehang Energy), a holding company of Turkey’s Chen Solar photovoltaic module and smart device manufacturer, has announced its plan to build a perovskite solar cell and module factory in Sichuan Province, China.
Fellow Energy had negotiated with the local government of Dechang County, Sichuan Province, for the construction of the project. It plans to build a solar cell factory to produce 2GW of perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells and 5GW of high-efficiency solar modules annually upon completion of the facility.
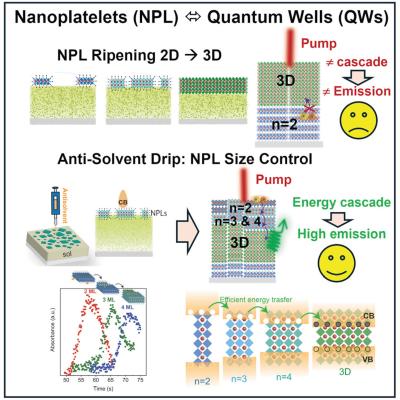
New method enables researchers to engineer layered perovskite materials at the atomic level
Researchers at North Carolina State University and Brookhaven National Laboratory have reported a technique for engineering layered hybrid perovskites (LHPs) down to the atomic level, which enables precise control on how the materials convert electrical charge into light.
Image credit: Matter
The technique opens the door to engineering materials tailored for use in next-generation printed LEDs, lasers and photovoltaic devices.
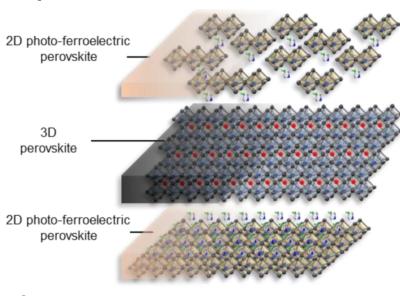
Researchers report photo-ferroelectric perovskite interfaces as a way to boost VOC in perovskite solar cells
Interface engineering plays a significant role in the constant improvement in the performance of perovskite photovoltaics, but such devices still suffer from several issues, including unavoidable open circuit voltage (VOC) losses. Now, an international team of researchers from Università Degli Studi Di Pavia, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), University of Cambridge, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT), Slovak Academy of Sciences and Imperial College London have proposed a different approach by creating a photo-ferroelectric perovskite interface.
Graphical representation of the 2D/3D/2D perovskite heterostructure. Image from: Nature Communications
By engineering an ultrathin ferroelectric two-dimensional perovskite (2D) which sandwiches a perovskite bulk, the scientists exploited the electric field generated by external polarization in the 2D layer to enhance charge separation and minimize interfacial recombination. As a result, they observed a net gain in the device VOC reaching 1.21 V, the highest value reported to date for highly efficient perovskite PVs, leading to a champion efficiency of 24%.
Halide Perovskite solar cells are shown to be ideal devices for in-sensor reservoir computing
As an increasing amount of multimodal sensors are used in intelligent electronics, energy expenditure gets more massive. Consequently, researchers aim to develop efficient computing paradigms or integrate energy harvesting from ambient sources. Halide perovskites possess unique photophysics and coupled ionic-electronic dynamics that actualize memory devices for brain-inspired computing. Synergizing the computing capability with their conventional light harvesting efficacy could address this issue.
Researchers from Singapore's Nanyang Technological University and Hong Kong's City University of Hong Kong recently examined the use of halide perovskite photovoltaics for in-sensor reservoir computing (RC).
Researchers use a self-assembled monolayer to fabricate 2D Ruddlesden-Popper perovskite solar cells with an efficiency exceeding 19 %
Two-dimensional Ruddlesden-Popper (2DRP) phase perovskites have excellent long-term environmental and structure stability. However, the efficiency of 2DRP perovskite solar cells (PSCs) still lags behind that of their 3D counterparts due to the large exciton binding energy between the large-volume organic spacer and the inorganic plate compared to their 3D analogs.
To address this issue, researchers from China's Northwestern Polytechnical University and Xijing University have used a thin layer of self-assembled monolayer material between the transporting layer and the perovskite film for efficient and stable 2DRP-based PSCs.
RenShine completes 1.2 MW perovskite distributed power station and connects it to the grid
Reports suggest that RenShine Solar has completed the construction of its 1.2 MW perovskite rooftop distributed power station. The plant is reportedly generating power and was connected to the grid on September 29.
The company says the plant’s power generation exceeded 3,000 kWh/day on its first day.
SolaEon Technology to launch 200MW + 1GW perovskite cell production lines
It was reported that SolaEon Technology, a Chinese manufacturer of next-gen solar cells with a focus on perovskite-based PV, recently signed an investment contract with the local government of Xuzhou City, China, as one of fifty-six contracts signed at the 27th Xuzhou Trade and Investment Fair.
SolaEon plans to invest about 1.2 billion yuan (almost USD$170 million) in the perovskite solar cell production base in the High-Tech Zone. Upon completion of the production lines with an annual capacity of 200MW and 1GW of perovskite cells, the production value is expected to reach 2 billion yuan (approximately USD$283 million) per year.
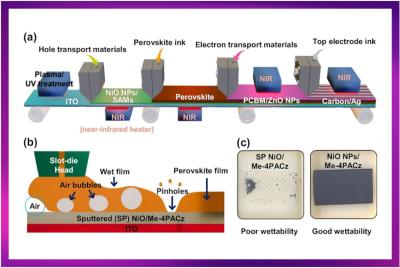
Researchers examine the influence of interfacial roughness on slot-die coatings for scaling-up perovskite solar cells
Slot-die coating (SDC) technology is a potential approach to mass produce large-area, high-performance perovskite solar cells (PSCs) at low cost. However, when the interface in contact with the perovskite ink has low wettability, the SDC cannot form a uniform pinhole-free perovskite film, which reduces the performance of the PSC.
Optimizing Slot-Die Coating for Commercial Solar Cell Production. Image credit: InfinityPV
Researchers from Korea's Jeonbuk National University have examined the correlation between interfacial roughness, wettability, and the overall efficiency of perovskite solar cells produced using slot-die-coating. This work offers a comprehensive understanding of how modifying the roughness of the hole transport layer (HTL) can improve the quality of perovskite films, enhance charge transport, and ultimately lead to high-efficiency perovskite solar cells with long-term stability.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 5
- Next page