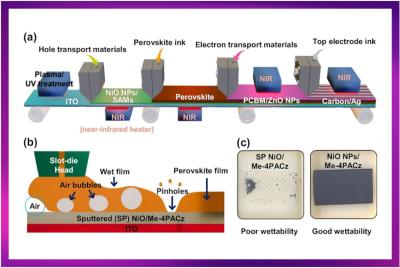
Slot-die coating (SDC) technology is a potential approach to mass produce large-area, high-performance perovskite solar cells (PSCs) at low cost. However, when the interface in contact with the perovskite ink has low wettability, the SDC cannot form a uniform pinhole-free perovskite film, which reduces the performance of the PSC.
Optimizing Slot-Die Coating for Commercial Solar Cell Production. Image credit: InfinityPV
Researchers from Korea's Jeonbuk National University have examined the correlation between interfacial roughness, wettability, and the overall efficiency of perovskite solar cells produced using slot-die-coating. This work offers a comprehensive understanding of how modifying the roughness of the hole transport layer (HTL) can improve the quality of perovskite films, enhance charge transport, and ultimately lead to high-efficiency perovskite solar cells with long-term stability.
The team found that increasing the roughness of the HTL improves wettability, allowing uniform perovskite films to form with fewer defects. By using slot-die coating-based HTL like NiOx/Me-4PACz, energy losses can be significantly suppressed, leading to higher power conversion efficiency (PCE). The study demonstrated that slot-die coating-produced perovskite solar cells can reach an impressive efficiency of 19.17% in unit cells, with long-term stability.
The team's findings suggest that the SDC process not only effectively eliminates the limitations associated with Me-4PACz, but also provides a promising approach for the sustained mass production of PSCs, which could lead to the fabrication of highly efficient perovskite solar modules and pave the way for future commercialization.