Perovskite Fuel Cells - Page 2
Researchers suggest ways to produce active and stable perovskite oxide-based OER materials
A study led by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has shown a shape-shifting quality in perovskite oxides that could be promising for speeding up the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) that is vital for hydrogen production (and a variety of other chemical processes). The research shows that perovskite oxides could be used to design new materials for making renewable fuels and also for storing energy.
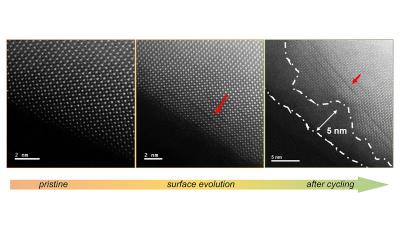 Surface evolution of a lanthanum cobalt oxide perovskite. Image credit: ANL
Surface evolution of a lanthanum cobalt oxide perovskite. Image credit: ANL
Perovskite oxides are less expensive than precious metals such as iridium or ruthenium that also promote OER. But perovskite oxides are not as active (in other words, efficient at accelerating the OER) as these metals, and they tend to slowly degrade.
Improving PV-based hydrogen generation with loss‐mitigation techniques
Researchers from the Australian National University (ANU) have quantified losses in PV'based solar hydrogen generation systems and have proposed a series of loss-mitigation techniques to improve solar'to'hydrogen (STH) conversion efficiencies.
The scientists identified STH efficiency as the crucial factor that needs to be improved to reduce the overall costs of PV-powered hydrogen generation. 'The U.S. Department of Energy has set a target of 20% STH efficiency by 2020 and an ultimate goal of 25%, to ensure the economic viability of PV'based solar hydrogen generation for large scale hydrogen production,' they specified, adding that current efficiency levels range from 10-15%.
UNIST researchers develop high-performance perovskite oxide catalysts using late transition metal oxide materials
A research team, jointly led by Professor Gun-Tae Kim and Professor Jun-Hee Lee in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at South-Korea's UNIST has succeeded in developing high-performance perovskite oxide catalysts using late transition metal oxide materials. In the process, the team discovered the reason behind the improved performance of both the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which has been explained by the change in the oxidation state of the transition metal caused by the increase in oxygen vacancies.
Perovskite oxide catalysts are composed of lanthanide, transition metal and oxygen. Owing to the excellent electrical conductivity and bifunctional ORR/OER activity, these catalysts have been considered to be an attractive candidate for metal-air batteries or fuel cells, in which opposite reactions, such as charging and discharging occur steadily. However, due to the high cost and low stability of noble metal catalysts, the development of alternatives is strongly desired.
ANU team pushes forward the efficiency of solar-to-hydrogen production
Australian National University (ANU) researchers have managed to push forward the efficiency of solar-to-hydrogen production that bypasses electrolysers and avoids AC/DC power conversion and transmission losses. They have recently managed to reach 17.6% efficiency, achieved with perovskite-silicon tandem absorbers, and they say their process is open to further refinement that could see clean hydrogen production become cost competitive with other fuels, including brown hydrogen and gas, more quickly than expected.
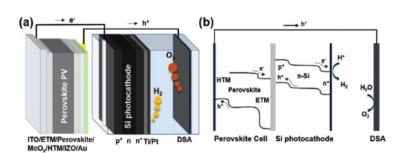 Perovskite-Si dual-absorber tandem PEC cell for self-driven water splitting. a) Schematic showing a perovskite solar cell wired to a Si photo-cathode in tandem, and a DSA anode. b) A representative general energy band diagram. Image: ANU
Perovskite-Si dual-absorber tandem PEC cell for self-driven water splitting. a) Schematic showing a perovskite solar cell wired to a Si photo-cathode in tandem, and a DSA anode. b) A representative general energy band diagram. Image: ANU
Australian National University (ANU) researchers, in a newly-released study lead by Dr. Siva Krishna Karuturi and Dr. Heping Shen, state that although PV modules have become a commercially viable method large-scale renewable energy generation, 'Achieving global renewable energy transition further relies on addressing the intermittency of solar electricity through the development of transportable energy storage means.'
INL team develops new perovskite-based electrode material for simpler hydrogen generation and energy storage
A team of researchers from Idaho National Laboratory (INL) has developed a new electrode material that simplifies hydrogen generation and energy storage via protonic, ceramic electrochemical cells (PCECs).
The INL team developed a perovskite-based oxygen electrode that not only enables operation at considerably lower temperatures than current technologies require (400'600ºC), but also exhibits 'triple-conducting' behavior ' it can conduct electrons, oxygen ions and protons within a PCEC.
A perovskite electrode may improve hydrogen production
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory (INL) have used an oxide of perovskite to create an oxygen electrode for use in electrochemical cells used for hydrolysis-based hydrogen production.
The researchers claim the perovskite oxide could help such cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity without additional hydrogen.
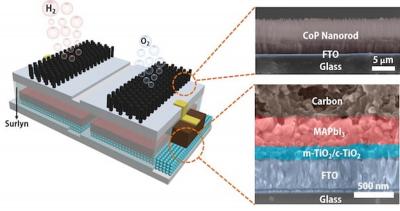
Rice scientists combine perovskite solar cells and catalytic electrodes to produce electricity
Rice University researchers have created an efficient, low-cost device that splits water to produce hydrogen fuel. The platform integrates catalytic electrodes and perovskite solar cells that, when triggered by sunlight, produce electricity. The current flows to the catalysts that turn water into hydrogen and oxygen, with a sunlight-to-hydrogen efficiency as high as 6.7%.
Hexagonal perovskites hold great potential for ceramic fuel cell technology
Researchers from the University of Aberdeen have reported that a new family of chemical compounds known as 'hexagonal perovskites' could be extremely beneficial for ceramic fuel cell technology and reducing global carbon emissions.
Ceramic fuel cells are highly efficient devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy and produce very low emissions if powered by hydrogen, providing a clean alternative to fossil fuels. Another advantage of ceramic fuel cells is that they can also use hydrocarbon fuels such as methane, meaning they can act as a 'bridging' technology which is an important asset in terms of the move away from hydrocarbons towards cleaner energy sources.
Perovskites found promising for low-temperature ammonia production
A team of researchers from Japan's Tokyo Tech have demonstrated perovskites' potential in the production of ammonia directly from hydrogen and nitrogen. This has the potential to open up a new approach to the manufacture of this industrially and agrochemically important gas. Ammonia is used widely an industrial reagent and in the formation of agricultural fertilizers, there are also examples of it being used as a "clean" energy carrier for hydrogen gas for fuel cells.
Masaaki Kitano and his team at Tokyo Tech point out that the main barrier to a facile synthesis of ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen gas is the surmounting the high energy barrier needed to split diatomic nitrogen. Nitrogen-fixing plants, of course, can handle this process with a range of enzymes evolved over millions of years and metals catalysts coupled with high temperatures and pressures are the mainstays of the industrial process. There have been efforts to make perovskites in which some of their oxygen atoms have been replaced with hydrogen and nitrogen ions to act as ammonia forming materials, but these too only work at a high temperature of more than 800 degrees Celsius and the reaction takes weeks to proceed to completion. These two factors had until now meant perovskites were not looking too promising as a way to create a new ammonia process.
Perovskite nickelates examined as a potential boost to electrocatalysis
Researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory are evaluating perovskite-structured rare-earth nickelates as alternatives to replace two reactions that are considered a challenge when it comes to electrocatalysts: the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Both are important for the development of better fuel cells, metal-air batteries, and electrolytic water-splitting.
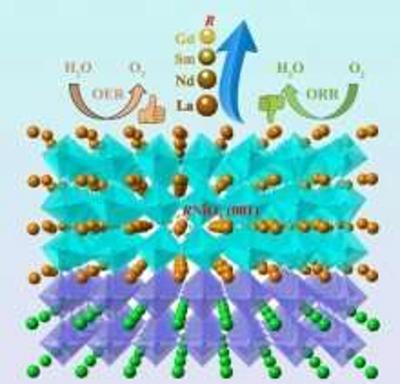
Materials such as platinum, iridium oxide and ruthenium oxide are well suited for these reactions, but they are scarce and expensive. The team has been working to study perovskite-structured rare-earth nickelates (RNiO3) that can serve as bifunctional catalysts capable of performing both OER and ORR.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page



