Sofab Inks develops and produces advanced materials for perovskite solar cells. The company's flagship product is a solvent-based tin oxide ETL that has already seen promising results in improving the performance and lifespan of perovskite solar cells. We interviewed the company's CEO Blake Martin and COO Jack Manzella, who help us understand the company's materials and business better. Click here to contact Sofab Inks to learn more or request a material sample.
Hello Blake and Jack. Earlier this year, Sofab Inks launched Tinfab, a high-performance and low-cost ETL material for perovskite solar cells. Can you detail the market reaction for your new material, and also the performance benefits that one can expect from this new ETL?
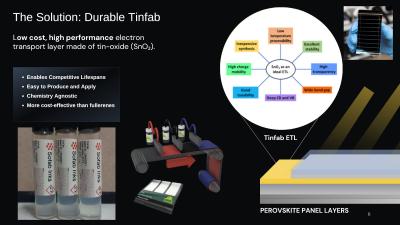
Since launching Tinfab, we’ve experienced significant interest across the industry, with approximately 40 companies and universities currently testing the material in perovskite solar cell applications. This strong engagement underscores the market's demand for innovative, scalable ETL solutions.
Tinfab is designed to fully replace C60/fullerenes in perovskite solar cells, addressing key limitations of C60, including lower stability, higher costs, and the complexity of vacuum deposition. Unlike C60, Tinfab can be solution-deposited in ambient environments, making it far more suitable for scalable manufacturing.
One of Tinfab’s standout features is its ability to be selectively doped, enabling precise tuning of energy band alignment to suit each manufacturer’s unique perovskite architecture. This flexibility, which is unmatched by competitors, allows manufacturers to tailor the material for their specific applications, reducing production costs and simplifying the transition from lab-scale to commercial manufacturing.
Early feedback from our collaborators and customers has been overwhelmingly positive. Our in-house testing has confirmed a solid 20% power conversion efficiency (PCE) on flexible substrates, and results from ongoing collaborations with industry leaders and academic institutions have surpassed this benchmark. Additionally, Tinfab demonstrates superior durability compared to C60, resisting degradation and offering more stable, long-lasting performance.
The enthusiastic market response reflects the increasing need for highly durable, scalable ETL materials. With itsadvanced capabilities and manufacturability, Tinfab is poised to play a leading role in driving the commercialization of perovskite solar technology.
Is the new ETL material also suitable for other perovskite devices, such as perovskite LEDs?
Yes, we designed Tinfab ETL with versatility in mind, making it suitable not only for perovskite solar cells but also for a range of emerging applications, including perovskite LEDs, quantum dots, organic photovoltaics (OPV), and gas sensors. Its electronic properties and excellent charge transport capabilities make Tinfab an ideal component for various optoelectronic devices, including LEDs, where efficient charge transfer is crucial.
Additionally, we see potential applications for our tin oxide material beyond perovskite devices, such as serving as an IR light blocker or as a catalyst in carbon capture processes.
Sofab is developing a nickel oxide hole transport material (HTL). Can you give us more details on this new material? How close is it to commercialization?
Our nickel oxide HTL represents an exciting addition to our product lineup, designed to offer higher stability and cost-efficiency compared to traditional HTLs like PTAA. We are still in the advanced development stages and expect to move closer to commercialization over the next few months. This material is being engineered for high compatibility with perovskite solar cells and other optoelectronic applications, enabling manufacturers to enhance device longevity without compromising on performance.
You are also launching a new aqueous-based SnO₂ to complement Sofab's flagship solvent-based SnO₂. Can you tell us more about this material and what it means for the perovskite industry?
Our aqueous-based SnO₂ is designed to provide a more regulatory friendly alternative to our solvent-based SnO₂. This new formulation addresses both environmental and regulatory challenges, offering manufacturers—whether in the perovskite industry or other sectors—a high-quality electron transport layer that integrates seamlessly into production lines.
As the perovskite industry moves toward commercial production, having an aqueous-based option ensures greater flexibility for safe, efficient, and compliant manufacturing processes. This development supports the industry’s push for sustainability and scalability while maintaining the performance standards our customers expect.
We understand one of Sofab’s goals is to replace C60 in perovskite solar panels with a next-generation alternative. While we know this is an early-stage effort, could you share more about it?
Our team spent years fabricating perovskite devices using C60, experiencing its limitations firsthand, particularly with stability, scalability, and cost. This challenge led us to investigate whether other manufacturers were facing similar issues, sparking our mission to develop a more effective alternative. The feedback we receive from customers highlights the industry’s frustration and strong interest in viable alternatives. One customer explained, “For the materials of ETL, [our company] is extremely interested in the replacement products of C60. In particular, in the case of PIN architecture, they really hope to consider competing products of C60.”
Customers frequently point out C60’s specific drawbacks, with one partner noting, “Nobody wants the C60 in there. It is mechanically fragile, serves as a delamination interface, and is expensive to get a stock of. C60 is the performance-limiting interface in the device.” Another customer shared concerns over scalability, stating, “The expense of using C60 in vacuum deposition is prohibitive at scale, and we’re actively seeking a more affordable alternative.”
For nearly two years, both our team and our key customers have fully transitioned from C60 to exclusively using Tinfab in perovskite solar cell fabrication. This shift has allowed us to enhance performance and reliability, overcoming the limitations of C60. One customer even referred to Tinfab as “a magic material” for its remarkable impact on device stability. By eliminating the need for C60 and offering a scalable, solution-deposited material, Tinfab enables manufacturers to overcome the common limitations of C60, helping them achieve more stable, efficient, and cost-effective production at commercial scale.
Sofab Inks aims to become a leading material supplier for perovskite solar panel producers. Can you share the company's short-term and long-term roadmaps?
In the short term, Sofab Inks is focused on expanding our product offerings to include complementary materials that address the evolving needs of perovskite solar cell manufacturers. We are making investments in our team and our ability to in-house perovskite module fabrication, accelerating our R&D process. Our immediate priorities include establishing strategic partnerships with manufacturers and equipment suppliers to facilitate seamless integration of our materials into large-scale production lines. We are also actively pursuing a series seed investment to support research, scale-up efforts, and cost reductions, enabling us to meet the growing demand from our customers.
Looking ahead, our long-term vision is to become a full-spectrum supplier for the perovskite industry. We aim to build a comprehensive portfolio of materials, including ETLs like Tinfab, HTLs such as our upcoming nickel oxide product, and next-generation materials for other critical layers in the cell. Beyond offering a diverse product line, we specialize in developing custom nanomaterials tailored to meet the specific needs of our customers, ensuring optimal performance for their unique applications.
An essential component of our roadmap is recognizing the vast depth of core competencies that perovskite solar cell manufacturers require to become successful ventures. This creates an opportunity for companies like ours to align seamlessly with their operations, addressing critical pain points around scaled ink synthesis. By leveraging our team’s technical expertise and deep understanding of customer’s manufacturing needs, we are well-positioned to proactively solve challenges and anticipate issues before they arise, ensuring a smoother path to scaling and commercialization.
Ultimately, our goal is to become the trusted go-to supplier for high-performance materials, driving perovskite solar technology toward its full commercial potential.
How do you view the perovskite industry? What will characterize the next few years as it moves from lab-scale to commercial-scale production?
The perovskite industry is on the cusp of a major transformation. Over the next few years, the focus will be on addressing challenges in scaling production, improving stability, and achieving cost-effectiveness. Transitioning from lab-scale research to commercial-scale production will require innovations in material stability, streamlined manufacturing processes, and reliable supply chains that deliver high-performance, economically viable materials.
China has emerged as a leader in perovskite solar manufacturing, leveraging its robust communication networks and track record in silicon solar. Their advancements in efficiency, stability over large areas, and field-tested modules have positioned them to accelerate the path to bankability for perovskite modules. Meanwhile, recent policy measures in the West present a competitive pathway for solar manufacturing, creating opportunities for emerging technologies like perovskites.
While the rollout of any new technology should be met with cautious optimism, the fundamental advantages of perovskites as a direct band-gap material—strategically better suited for solar applications—remain compelling. The promise of long-term cost reductions, coupled with perovskites' versatility across multiple applications, supports a strong case for their inevitable role as either a complement to or a replacement for incumbent technologies.
We are already seeing industrial-scale installations of perovskite panels from pioneers such as GCL, Oxford PV, and Microquanta. Success at these sites will validate the technology, encouraging early adopters and driving demand across the supply chain. This will prompt suppliers, equipment manufacturers, and research institutions to secure positions upstream. Critical materials like silver and lead will be closely monitored, while tandem companies with secure access to silicon modules will hold a distinct advantage, particularly given the reliance on silicon from China or the higher costs of Western silicon modules.
Sofab Inks aims to play a pivotal role in this transition. We are committed to providing materials that not only meet the industry’s high-performance demands but are also optimized for large-scale, economically viable production. We foresee increased collaborations across the supply chain, from partnerships with equipment manufacturers to joint initiatives with research institutions. By being at the forefront of this shift, Sofab is well-positioned to support the commercialization of perovskite solar technology and its broader adoption across the energy sector.
Where do you see the main value of perovskite PVs in the near future? Will that be in utility-grade solar, or in novel applications such as BIPVs, indoor solar, agri-PVs, etc.?
Perovskite PVs offer a level of versatility that traditional silicon solar technology struggles to match. While utility-grade applications will remain a significant market—especially as tandem perovskite-silicon solar panels gain traction—the true potential of perovskites lies in their adaptability for novel applications.
Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPVs) and indoor solar are particularly promising, as perovskites excel in customizable form factors and maintain strong performance under low-light conditions. Their lightweight and flexible nature also makes them ideal for terrestrial, automotive, and IoT markets. In the near future, we anticipate the commercialization of these exciting applications, which will push solar energy into spaces previously considered impractical for traditional solar panels.
From a performance standpoint, the theoretical efficiency for a single-junction module is around 33%, while dual-junction modules, like perovskite-silicon tandems, could achieve 40–42%. To put that in perspective, every 1% increase in module efficiency can reduce the capital cost of a solar plant by approximately $0.01–$0.03 per watt. For a 100 MW solar installation, that translates to $1–$3 million in cost savings per percentage point of increased efficiency.
Overall, we believe perovskite technology’s adaptability will make it an invaluable solution for applications where traditional solar panels are less effective. Sofab Inks is committed to supporting this transition with materials designed for diverse applications, expanding the reach and impact of perovskite solar technology.
Blake Martin is the CEO and co-founder of Sofab Inks, where he drives the development of nanoparticle materials for renewable energy and industrial applications. With a Ph.D. in Chemical Engineering and expertise in scalable perovskite solar technologies, he has led Sofab to global partnerships, industrial-scale production, and multiple patent filings.
Jack Manzella is the Chief Operating Officer and co-founder of Sofab Inks, where he manages business development, finances, and operational stability. Jack’s background includes leading commercialization strategy at General Electric's R&D lab, and he holds an MBA in Innovation.
About SoFab Inks
Sofab Inks Inc. is a pioneering chemical manufacturing startup specializing in advanced materials for perovskite solar cells. Established by a team of experts with a combined 35 years of industry experience in perovskite technology, Sofab stands out for its ability to custom-design materials that seamlessly integrate with each manufacturer’s unique perovskite architecture.
Sofab’s flagship product is Tinfab, a breakthrough solvent-based tin oxide electron transport layer (ETL) that has already seen promising results in improving the performance and lifespan of perovskite solar cells. This innovation, along with Sofab’s expanding product portfolio, has positioned the company as a crucial player in the transition of perovskite technology from lab-scale to commercial-scale applications.
Currently, Sofab Inks collaborates with approximately 40-50 companies and universities globally, with several of these customers progressing to production stages. In addition to Sofab’s solvent-based tin oxide ETL, Sofab is developing a nickel oxide hole transport material and a new aqueous-based SnO₂ that will complement its solvent-based counterpart. These advancements aim to address key industry needs and improve durability and scalability in perovskite manufacturing.
Ready to explore the possibilities of perovskites? Contact us today to learn more or request a material sample.