Researchers optimize a blade coating process to achieve 12.6%-efficient nickel oxide-based large-area perovskite solar modules
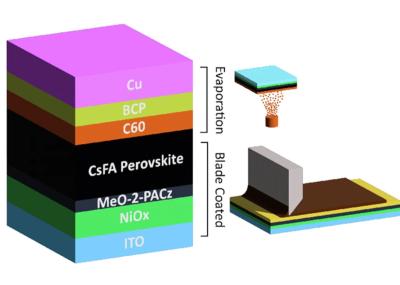
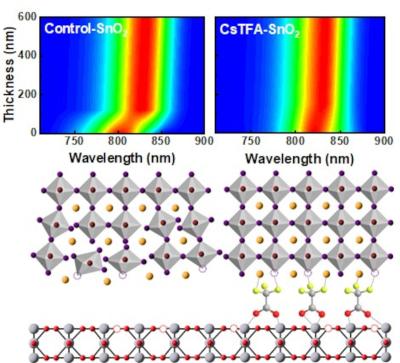
Researchers from CHOSE (Centre for Hybrid and Organic Solar Energy) at Tor Vergata University of Rome, CNR-ISM and Saule Technologies have introduced an optimized blade coating process for the scalable fabrication of large-area (15 cm × 15 cm) perovskite solar modules with a nickel oxide hole transport layer, performed in ambient air and utilizing a non-toxic solvent system.
The research group fabricated a 110 cm² perovskite solar module with an inverted configuration and a hole transport layer that uses nickel oxide instead of commonly utilized poly(triarylamine) (PTAA). The proposed architecture aims to achieve high efficiency that is competitive with PTAA-based panels while improving stability.