New collaborative research center to be funded and established in order to push tandem solar modules forward
The U.S. Department of Energy Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) has announced that a team of researchers, led by MIT and including the University of California San Diego, has been selected to receive a $11.25 Million cost-shared award to establish a new research center that will advance the development of next-generation solar cells for commercial use.
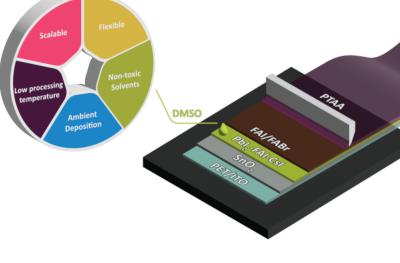
A collaborative effort with CubicPV, solar startup Verde Technologies, and Princeton University, the center will bring together teams of researchers to support the creation of perovskite-silicon tandem solar modules. These are solar cells made of stacked materials—silicon paired with perovskites—that together absorb more of the solar spectrum than single materials, resulting in a dramatic increase in efficiency. Their potential to generate significantly more power than conventional solar cells could make a meaningful difference in the race to combat climate change and the transition to a clean-energy future.