Art-PV India receives $10 Million grant for silicon/CdTe-perovskite tandem solar cells
Art-PV India, an IIT Bombay-incubated start-up, has been awarded a $10 million grant by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE). The funding will enable the company to set up a manufacturing plant for high-efficiency tandem solar cells.
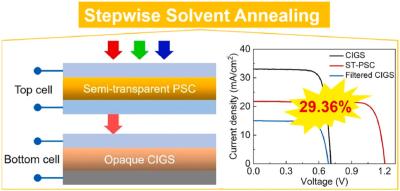
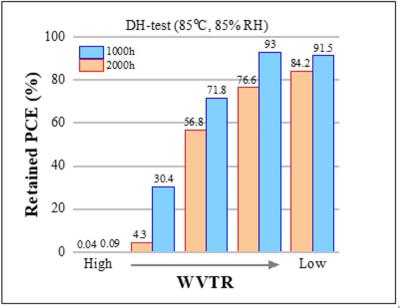
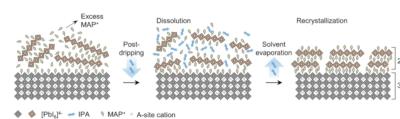
Art-PV has developed a 2-Terminal Monolithic Silicon/CdTe-Perovskite tandem solar cell that boasts an impressive 29.8% efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. The cell is constructed with a silicon base, topped with layers of cadmium telluride (CdTe) and a perovskite-structured material.