Researchers identify the potential of hexagonal perovskite oxides for next-gen protonic ceramic fuel cells
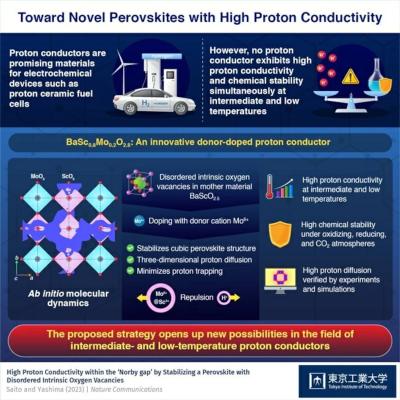
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology and Tohoku University have reported hexagonal perovskite-related oxides with exceptionally high proton conductivity and thermal stability.
The team explained that these materials' unique crystal structure and large number of oxygen vacancies enable full hydration and high proton diffusion, making them ideal candidates as electrolytes for next-generation protonic ceramic fuel cells that can operate at intermediate temperatures without degradation.