Novel bioinspired multidentate-cross-linking strategy enables highly stable flexible perovskite photovoltaics
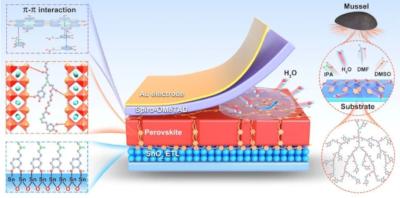
Researchers from China's Northwestern Polytechnical University, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Henan University have addressed the stability challenge of flexible perovskite solar cells (FPSCs). Inspired by the exceptional wet adhesion of marine mussels via adhesive proteins (dopamine, DOPA), the scientists proposed a multidentate-cross-linking strategy, which combines multibranched structure and adequate dopamine anchor sites in three-dimensional hyperbranched polymer to directly chelate perovskite materials in multiple directions.
Schematics of key components for the underwater adhesion feature of marine mussels and HPDA adhesive in perovskite films and interfaces. Image from: Nature Communications
This constructs a vertical scaffold across the bulk of perovskite films from the bottom to the top interfaces, that intimately binds to the perovskite grains and substrates with a strong adhesion ability, and enhances mechanical durability under high humidity.