Researchers develop strategy to reduce the formation of anions vacancy defects in halide perovskite solar cells
Researchers at China's Shaanxi Normal University and Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have designed a novel strategy to reduce the formation of anions vacancy defects in halide perovskite solar cells. The team reported that the new approach results in higher efficiency and remarkable stability.
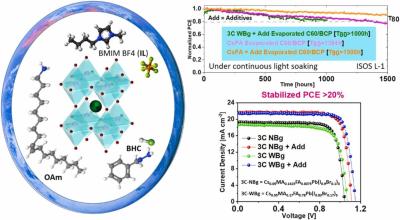
The new method, which they defined as 'a one-stone-for-two-birds' strategy, utilized a ligand known as 3-amidinopyridine (3AP) to pin anions in the device. Anions can control the nucleation and growth of the perovskite crystals and act as a passivating agent to improve the crystallinity, thus ensuring improved efficiency. The team says the 3AP molecules deposited on the perovskite layer are able to form strong chemical bonds with the cell's lead(II) iodide (Pb–I) interlayer and, as a consequence, create a sustainable pinning effect.