Versatile SnO2 inks boost PSC efficiency across multiple solar cell architectures
Recently, a University of Louisville team of researchers used nanoparticle inks by Sofab Inks (a U of Louisville spinout) to create PSCs with ~20% PCE on flexible substrates. Their study addresses the solvent scope and perovskite compatibility of acetate-stabilized yttrium-doped SnO2 (Y:SnO2) dispersions.
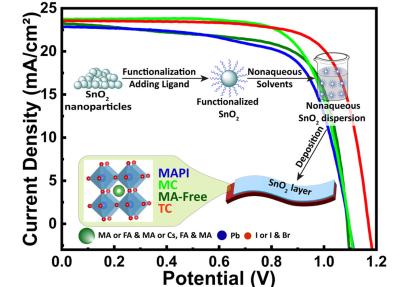
Tin oxide (SnO2) stands out as a compelling electron transport material (ETM) for perovskite solar cells (PSCs), boasting exceptional optoelectronic properties, coupled with low-temperature solution processability, cost-effectiveness, and remarkable stability. However, the widespread application of SnO2 has been hindered by solvent incompatibilities, limiting its use to devices where it is deposited beneath the perovskite layer. To unlock the full potential of SnO2 and expand its use across various device structures, including inverted PSCs and tandem devices, innovative deposition strategies will need to be developed. These advancements could pave the way for more efficient and versatile solar cell designs, pushing the field of photovoltaics forward.
The scientists showed that dispersions in several lower alcohols and select polar aprotic solvents can be directly deposited on perovskite using scalable and low-temperature processes. In addition, they are compatible with various perovskite formulations, including those with mixed cations and mixed anions.