Perovskite Solar - Page 17
Jinko Solar announces N-type TOPCon-based perovskite tandem solar cell with 33.24% efficiency
China-based global PV and ESS supplier, Jinko Solar, has announced a significant breakthrough in the development of its N-type TOPCon-based perovskite tandem solar cell.
Tested by the Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, the cell reportedly achieved an impressive conversion efficiency of 33.24%. This enhancement surpasses JinkoSolar's previous record of 32.33% for the same type of tandem cells.
Renshine plans GW-scale perovskite PV panel factory
It was reported that Renshine Solar will open a gigawatt-scale perovskite PV module factory in Jiangsu province, with a planned investment of CNY 1 billion ($138 million).
The CNY 1 billion gigawatt-scale perovskite cell project will be located in the Economic and Technological Development Zone (ETDZ) in Changshu, Jiangsu province, China. The Company started operating a 150 MW production line for perovskite modules in January. It has since claimed that its commercial modules have achieved a power conversion efficiency of 18.4%.
Researchers set efficiency record for stable multipodal self-assembled molecule-based perovskite solar cell
Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Japan's Yamagata University, developed three isomeric bisphosphonate-anchored self-assembled molecules (SAMs) to achieve highly efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells (PSCs).
The wettability, absorbability and compactness of SAMs, which are used as hole-transporting layers (HTLs) for PSCs, critically affect the efficiency and stability of the devices. Therefore, the researchers proposed a molecular strategy to synthesize three bisphosphonate-anchored indolocarbazole (IDCz)-derived SAMs, namely IDCz-1, IDCz-2, and IDCz-3. The three SAMs with different positions of the two nitrogen atoms in the IDCz unit were each employed on conductive oxide substrates for inverted PSCs.
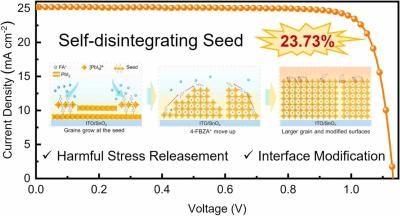
Researchers use 'self-disintegrating seed' strategy to design perovskite solar cell with 23.73% efficiency and impressive stability and fill factor
Researchers from China's Southwest Petroleum University, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing University, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology and Tongwei Solar have designed a perovskite solar cell with remarkable perovskite film quality through the 'self-disintegrating seed' strategy. The device achieved both an impressive fill factor values and remarkable stability.
The researchers, in fact, report what they say is one of the highest fill factor values ever achieved for a perovskite solar cell, by reducing its nonradiative recombination and residual stress through what they called a self-disintegrating seed strategy.
Australia allocates funds to support U of Queensland project on perovskite solar cells
Funding totaling AUD$58.3 million (over USD$38,781,000) has been announced through a recent round of the Australian Laureate Fellowships scheme, supporting projects including quantum computing devices, more durable perovskite-based solar photovoltaic cells, and terahertz biosensing.
The funding was announced through the scheme, which is part of ARC’s Discovery Program and supports researchers “to design ambitious research programs around a team of postdoctoral fellows and postgraduate students” in various fields.
Researchers develop thermal regulation strategy to improve stability and efficiency in all-perovskite tandem solar cells
Researchers at China's Qingdao University of Science and Technology and Canada's University of Toronto have developed a thermal regulation strategy by incorporating carboranes into perovskites to improve the performance of inverted tin-lead perovskite tech for all-perovskite tandem solar cells.
The Chinese-Canadian research group has designed a monolithic all-perovskite tandem solar cell that utilizes a top inverted perovskite PV device based on an absorber made with mixed tin-lead (Sn-Pb) perovskite via the newly developed thermal regulation strategy.
Researchers manage to reach 14.15% efficiency of carbon-based perovskite solar cell without hole transport layer
Researchers from China's Beihang University and Changchun University of Technology have developed a new surface engineering strategy to build low-cost solar cells without a hole transport layer. The devices were treated with benzoylcholine halide to reduce non-radiation recombination and achieved impressive efficiency and stability.
The research group developed a carbon-based all-inorganic perovskite solar cell without the use of an expensive hole transport layer (HTL). In the proposed cell architecture, the absence of the HTL, which prevents direct contact between the carbon electrode and the perovskite, is compensated by engineering the surface composition of the perovskite film. ”The bipolar transport of the perovskite layer and the hole extraction ability of the carbon electrode provide a theoretical basis for the preparation of HTL-free CsPbI2Br carbon-based all-inorganic perovskite solar cells,” the researchers said in their study.
Researchers use machine learning to accelerate the discovery of perovskite materials
Researchers at EPFL, Shanghai University and Université catholique de Louvain recently developed a method based on machine-learning to quickly and accurately search large databases, leading to the discovery of 14 new materials for solar cells.
The research project, led by EPFL's Haiyuan Wang and Alfredo Pasquarello, developed a method that combines advanced computational techniques with machine-learning to search for optimal perovskite materials for photovoltaic applications. The approach could lead to more efficient and cheaper solar panels, transforming solar industry standards.
Microquanta moves towards scale-up with SMIT Thermal Solutions' equipment for GW perovskite factory
Microquanta, a perovskite solar cell manufacturer based in Hangzhou, China, has announced its latest procurement of state-of-the-art vacuum deposition equipment from SMIT Thermal Solutions. This significant acquisition, surpassing 9 million Euros in value, marks a pivotal moment in Microquanta's journey towards launching the world's first gigawatt-scale (GW) perovskite solar cell factory in Hangzhou.
This collaboration with SMIT Thermal Solutions is not a first for Microquanta; the Dutch-based company has been a partner since 2018, starting with a pilot setup, followed by the delivery of a mass production system for Microquanta's 100MW factory. The latest deal involves cutting-edge next-generation mass production systems, tailored to meet the ambitious scale and efficiency goals of Microquanta's GW factory.
Researchers develop strategy based on SAMs to design inverted PSC with 24.38% efficiency
Researchers from China's Hangzhou Dianzi University and Jiaxing University have developed a strategy for optimizing the bottom region of perovskite solar cells and designed an inverted perovskite solar cell using the new strategy. The proposed cell was treated with two molecules known as 2-mercaptoimidazole and 2-mercaptobenzimidazole and was based on a hole transport layer relying on a self-assembled monolayer.
“The HTLs prepared with SAM materials not only have negligible parasitic absorption, low material consumption, and stable adhesion but also exhibit inherent passivation of defects on the bottom of perovskites,” the research team explained.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 17
- Next page