Perovskite Solar - Page 2
UtmoLight develops 450W perovskite solar module with 16.1% efficiency
It was reported that China-based UtmoLight has developed a 450 W perovskite solar module with a 16.1% efficiency rating. It claims that the panel is currently the largest perovskite PV module available.

The new module reportedly covers an area of 2.8 square meters, uses dual-glass encapsulation and features an open-circuit voltage of 190.7 V, a short-circuit current of 3.19, and a fill factor of 73.7%.
Researchers tweak perovskite precursor solutions to produce useful cations that improve perovskite solar modules
Researchers from Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), North China Electric Power University, Westlake University, Lomonosov Moscow State University and others have described the addition of N,N-dimethylmethyleneiminium chloride ([Dmei]Cl) into perovskite precursor solutions to produce two cations in situ—namely 3-methyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,3,5-triazin-1-ium ([MTTZ]+) and dimethylammonium ([DMA]+) cations - that enhanced the photovoltaic
performance and stability of perovskite solar modules.
A schematic of the roles of [MTTZ]+ and [DMA]+ in the 3D perovskite matrix. Image from: Science
The team explained that the in situ formation of [MTTZ]+ cation increased the formation energy of iodine vacancies and enhanced the migration energy barrier of iodide and cesium ions, which suppressed nonradiative recombination, thermal decomposition, and phase segregation processes.
Researchers examine homogeneous 2D perovskite passivation layer and achieve positive results
The formation of a homogeneous passivation layer based on phase-pure two-dimensional (2D) perovskites is a challenge for perovskite solar cells, especially when upscaling the devices to modules. Researchers from China's Wuhan University of Technology, Xidian University, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China and Germany's Technical University of Munich have revealed a chain-length-dependent and halide-related phase separation problem of 2D perovskite growing on top of three-dimensional perovskites.
The scientists have demonstrated that a homogeneous 2D perovskite passivation layer can be formed upon treatment of the perovskite layer with formamidinium bromide in long-chain ( >10) alkylamine ligand salts.
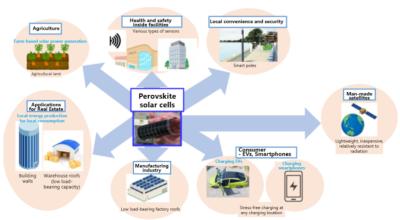
MOL PLUS to invest in EneCoat Technologies
MOL PLUS has announced its intent to invest in EneCoat Technologies, a spin-off company from Kyoto University that develops perovskite solar cells and related materials.
MOL PLUS stated it is "pleased to participate in this fundraising" and views the widespread use of perovskite solar cells as a revolutionary solution that will enable power generation anywhere, indoors or outdoors. Moving forward, the MOL Group plans to study a wide range of applications in the port, logistics, and real property fields, including installation on the decks of freighters and on the roofs and walls of port facilities such as warehouses and terminal cargo handling centers.
Microquanta announces 23.65% efficiency of small-size perovskite module
Microquanta has reportedly achieved a conversion efficiency of 23.65% on small perovskite solar modules, certified by Fujian Metrology Institute.
The perovskite module has an area of 19.38 cm², achieved using its proprietary frozen laser repair technology. It is said to exhibit exceptional photo-thermal durability, with less than 5% efficiency degradation even after exposure to cumulative UV aging doses far exceeding the IEC 61215 standard (200 kWh).
Researchers use copper thiocyanate to develop efficient and stable perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells
Researchers from Zhejiang University, Soochow University, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and Suzhou Maxwell Technologies have addressed common challenges related to hole transport layers that are commonly used for the perovskite top cells, such as defects, non-conformal deposition or de-wetting of the overlying perovskite on the textured silicon bottom cells.
The team decided to develop a strategy based on co-deposition of copper(I) thiocyanate and perovskite, where effective perovskite grain boundary passivation and efficient hole collection are simultaneously achieved by the embedded copper(I) thiocyanate, which creates local hole-collecting contacts. Fabricated monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem devices achieved a certified power conversion efficiency of 31.46% for 1 cm2 area devices.
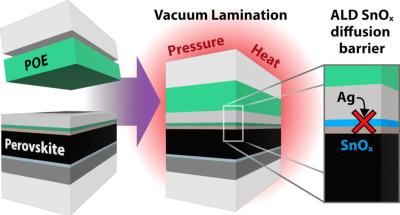
New method can reduce thermal degradation of PSCs during vacuum lamination
Current photovoltaic (PV) panels typically contain interconnected solar cells that are vacuum laminated with a polymer encapsulant between two pieces of glass or glass with a polymer backsheet. This packaging approach is common in conventional photovoltaic technologies such as silicon and thin-film solar modules, contributing to thermal management, mechanical reinforcement, and environmental protection to enable long lifetimes. Commercial vacuum lamination processes typically occur at 150 °C to ensure cross-linking and/or glass bonding of the encapsulant to the glass and PV cells. Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are known to degrade under thermal stresses, especially at temperatures above 100 °C.
Researchers from NREL and The Dow Chemical Company have examined degradation modes during lamination and developed internal diffusion barriers within the PSC to withstand the harsh thermal conditions of vacuum lamination.
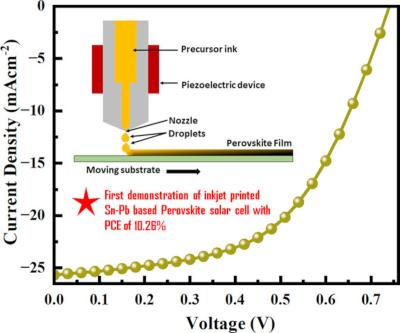
Researchers develop strategy for inkjet printing lead-reduced, eco-friendly perovskite solar cells
A Research Group led by Prof. Eva Unger at Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB), in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay and University of Jammu, has reported the use of inkjet printing to fabricate thin films of combinatorial mixed formamidinium tin-lead perovskites and evaluated their layer quality and device performance. The team focused on optimizing the inkjet-printing process to ensure precise film deposition and enhance device performance.
Image credit: ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces
The scientists deposited Sn/Pb intermixed FASn1–xPbxI3 (x = 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75)-based perovskite thin films through inkjet printing. The study focused on finding the ideal composition ratio for a favorable photovoltaic performance. The deposited FASn1–xPbxI3 thin films were subjected to various characterizations followed by their implementation in solar cells.
Japanese Government to fund perovskite solar cell demonstration project
It was reported that Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) have decided to support a demonstration project for perovskite solar cells conducted by Sekisui Chemical and Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (HD).
The total project cost is estimated at about 18.3 billion yen ( just under USD$119,000,000), with approximately 12.5 billion yen (around USD$81 million) to be subsidized through the Green Innovation (GI) Fund project. The project will verify installation methods, construction methods, and mass production technologies that take advantage of the unique characteristics of perovskite solar cells.
New approach enables all-perovskite tandem solar cell with 28.2% efficiency
The certified efficiency of 1 cm2 scale all-perovskite tandem solar cells tends to lag behind that of their small-area (~0.1 cm2) counterparts. This performance deficit originates from inhomogeneity in wide-bandgap (WBG) perovskite solar cells (PSCs) at a large scale. The inhomogeneity is thought to be introduced at the bottom interface and within the perovskite bulk itself.
Researchers from Nanjing University, Jilin University, University of Cambridge, University of Victoria, The Australian National University, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Renshine Solar (Suzhou) have reported an all-perovskite tandem solar cell based on a wide-bandgap top perovskite cell with a 20.5% efficiency.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page