Multifunctional sulfur-based additives could improve perovskite solar cells' efficiency and moisture stability
Aiming to explore the potential of sulfur-based additives for increasing both device power conversion efficiency and moisture stability of perovskite solar cells, researchers from BCMaterials (Spain), Huazhong University of Science and Technology (China), Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (Germany) and CNRS (France) have reported a mechanism for the local nanoscopic humidity ingression into a multifunctional additiviated formamidinium-loaded halide perovskites.
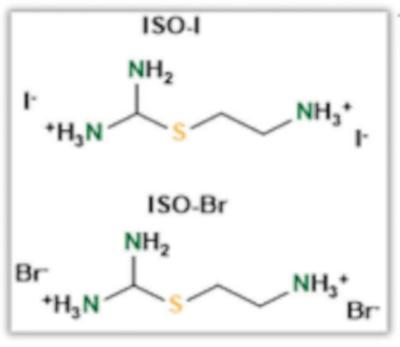
a) The molecular structure of additives used. Image from: Advanced Energy Materials
By tuning the iodide and bromide tails of the additives, the influence of sulfur heteroatom containing ammonium-amidinium salts on the photo-physical and device properties of a formamidinium-rich perovskite absorber was uncovered.