Researchers develop improved perovskite solar cell using a uniform sub-nanometer dipole layer
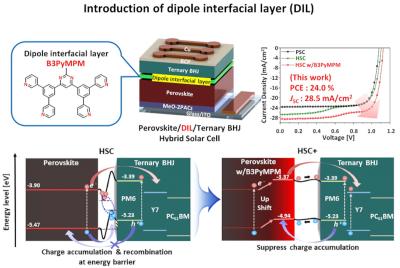
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Yonsei University, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) and Korea Institute of Ceramic Engineering and Technology (KICET) have reported a high-efficiency and high-stability organic-inorganic hybrid solar cell production technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture beyond the existing visible light range.
The research team suggested a hybrid next-generation device structure with organic photo-semiconductors that complements perovskite materials limited to visible light absorption and expands the absorption range to near-infrared. In addition, they focused on a common issue that mainly occurs in the structure and developed a solution to this problem by introducing a dipole layer - a thin material layer that controls the energy level within the device to facilitate charge transport and forms an interface potential difference to improve device performance.