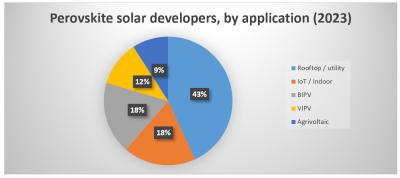
Researchers report perovskite solar cell with ultrathin protective TMO buffer layers
Researchers from the University of Rome Tor Vergata, ENEA and CNR-ISM have used protective buffer layers in perovskite solar cells to mitigate damage during the sputtering of indium tin oxide in the production process. The scientists claim the buffer layers were able to achieve this without damaging the cell’s average visible transmittance.
The cell utilizes buffer layers made of transition metal oxides (TMOs) intended to protect the cell during the sputtering of indium tin oxide (ITO) in the cell production process. The scientists tested, in particular, two different evaporated transition metal oxides (TMOs) – molybdenum oxide (MoOx) and vanadium oxide (V2Ox) and found the former provided the best performance.