Researchers develop thermal regulation strategy to improve stability and efficiency in all-perovskite tandem solar cells
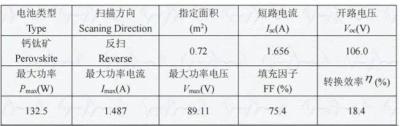
Researchers at China's Qingdao University of Science and Technology and Canada's University of Toronto have developed a thermal regulation strategy by incorporating carboranes into perovskites to improve the performance of inverted tin-lead perovskite tech for all-perovskite tandem solar cells.
The Chinese-Canadian research group has designed a monolithic all-perovskite tandem solar cell that utilizes a top inverted perovskite PV device based on an absorber made with mixed tin-lead (Sn-Pb) perovskite via the newly developed thermal regulation strategy.