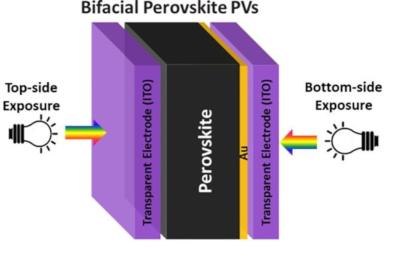
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Mandi (IIT-Mandi), the National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) and China's Guangxi University have designed efficient indoor bifacial perovskite photovoltaics (i-BPPVs) with the capability of harvesting maximum light from both top and bottom sides. This achievement could be a significant step towards advancing cost-effective and efficient technology for harvesting more energy from artificial indoor light sources.
The i-BPPVs were designed and fabricated in a stack of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite material amid a transparent bottom electrode (ITO), and top (Au/ITO) electrode. The fabricated i-BPPVs exhibited an efficiency of 30.3%, short circuit current density (JSC) of 148.3 µA cm−2, open circuit voltage (VOC) of 0.93 V, and fill factor (FF) of 71.7% when artificial LED light source of 1000 lx is exposed from the top side, whereas an efficiency of 22.1%, JSC of 116.2 µA cm−2, VOC of 0.89 V, and FF of 69.4% have been obtained from the bottom side.
The champion bifacial i-BPPVs reportedly display an excellent bifaciality factor (Φ) of 0.73 and demonstrated superior operational stability when subjected to continuous illumination.