Researchers design efficient inverted perovskite solar cells using a synergistic bimolecular interlayer
A team of researchers, led by the Fudan University in China, has developed a p-i-n structure inverted perovskite solar cell that uses a synergistic bimolecular interlayer (SBI) and achieves what the team says is the smallest nonradiative recombination induced open-circuit voltage loss ever reported.
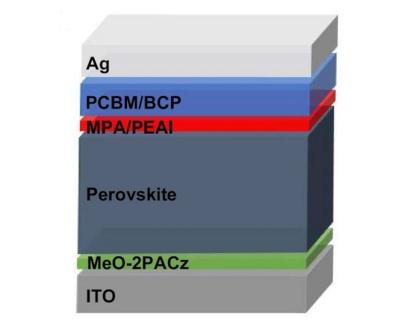
Schematic illustration of p-i-n PSC using MPA/PEAI as SBI. Image from Nature Communications
The researchers' SBI strategy consisted of depositing 4-methoxyphenylphosphonic acid (MPA) and 2-phenylethylammonium iodide (PEAI) as modulators to functionalize the perovskite surface.