Researchers demonstrate how potassium trifluoromethanesulfonate can improve perovskite solar cells
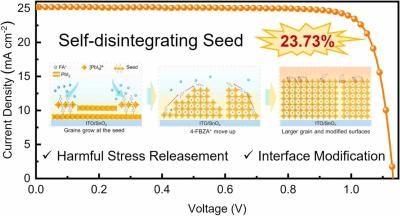
Researchers at China's Hangzhou Dianzi University have modified the absorber of a conventional perovskite solar cell with potassium trifluoromethanesulfonate (KTFS) and found that the additive improved the device's performance and stability. The cell’s perovskite film reportedly showed less lead defects and lower J-V hysteresis.
“The KTFS molecule is a typical kind of potassium salt including the cationic potassium (K+) and anionic trifluoromethanesulfonate (SO3CF3−), indicating a bifunctional interaction between KTFS and perovskite,” the team explained. “The sulfonyl group can passivate the undercoordinated lead of the deep-level defect and thus inhibit the non-radiative recombination.”