Researchers develop perovskite solar panels with a thermally stable device stack
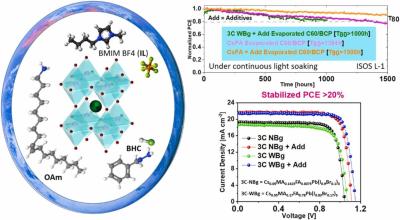
A research team led by Imec, that also included teams from Hasselt University and Kuwait University, has fabricated a perovskite solar module based on a scalable, stable device stack that can be processed with industry-compatible techniques, such as sputtering, evaporation, and slot-die coating.
The panel is based on 17%-efficient perovskite solar cells built with a p-i-n configuration, an electron transport layer made of nickel(II) oxide (NiOx), a perovskite layer deposited via slot-die coating, an electron transport layer made of buckminsterfullerene (C60) and lithium fluoride (LiF), a bathocuproine (BCP) buffer layer, and a copper (Cu) electrode.