Double layer SiO2-coated water-stable halide perovskites show potential as antimicrobial agents
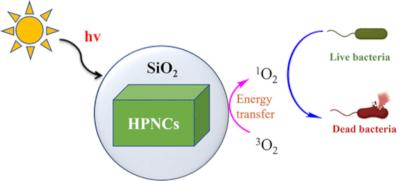
Rice University researchers have developed highly water-stable SiO2-coated halide perovskite nanocrystals (HPNCs) as efficient photocatalysts for antimicrobial applications. The double SiO2 layer coating method confers long-term structural and optical stability to HPNCs in water, while the in situ synthesis of lead- and bismuth-based perovskite NCs into the SiO2 shell enhances their versatility and tunability.
Image from: Nano Letters
The team demonstrated that the substantial generation of singlet oxygen via energy transfer from HPNCs enables efficient photoinduced antibacterial efficacy under aqueous conditions. More than 90% of Escherichia coli was inactivated under mild visible light irradiation for 6 h. The excellent photocatalytic antibacterial performance suggests that SiO2-coated HPNCs hold great potential for various aqueous phase photocatalytic applications.