Researchers design unique passivation that enables stable perovskite solar cells with low photovoltage loss
Researchers from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Oxford University and the University of Sheffield have developed a molecular treatment that significantly enhances the efficiency and durability of perovskite solar cells.
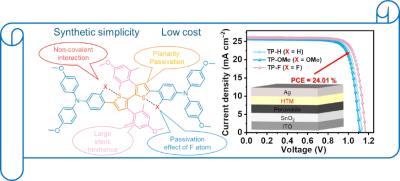
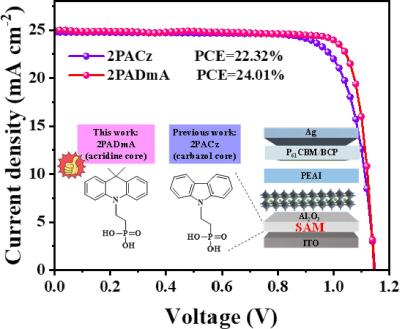
A key to the solution was their successful identification of critical parameters that determine the performance and lifespan of halide perovskites. The research team investigated various ways of passivation, a chemical process that reduces the number of defects or mitigates their impact in materials, thereby enhancing the performance and longevity of devices comprising these materials. They focused on the “amino-silane” molecular family for passivating perovskite solar cells.